Properties & Qualities
Application
Accessories Art Clothing Furnishing
Qualities
2D Colourful Flexible Smooth Textured / tactile
Colour
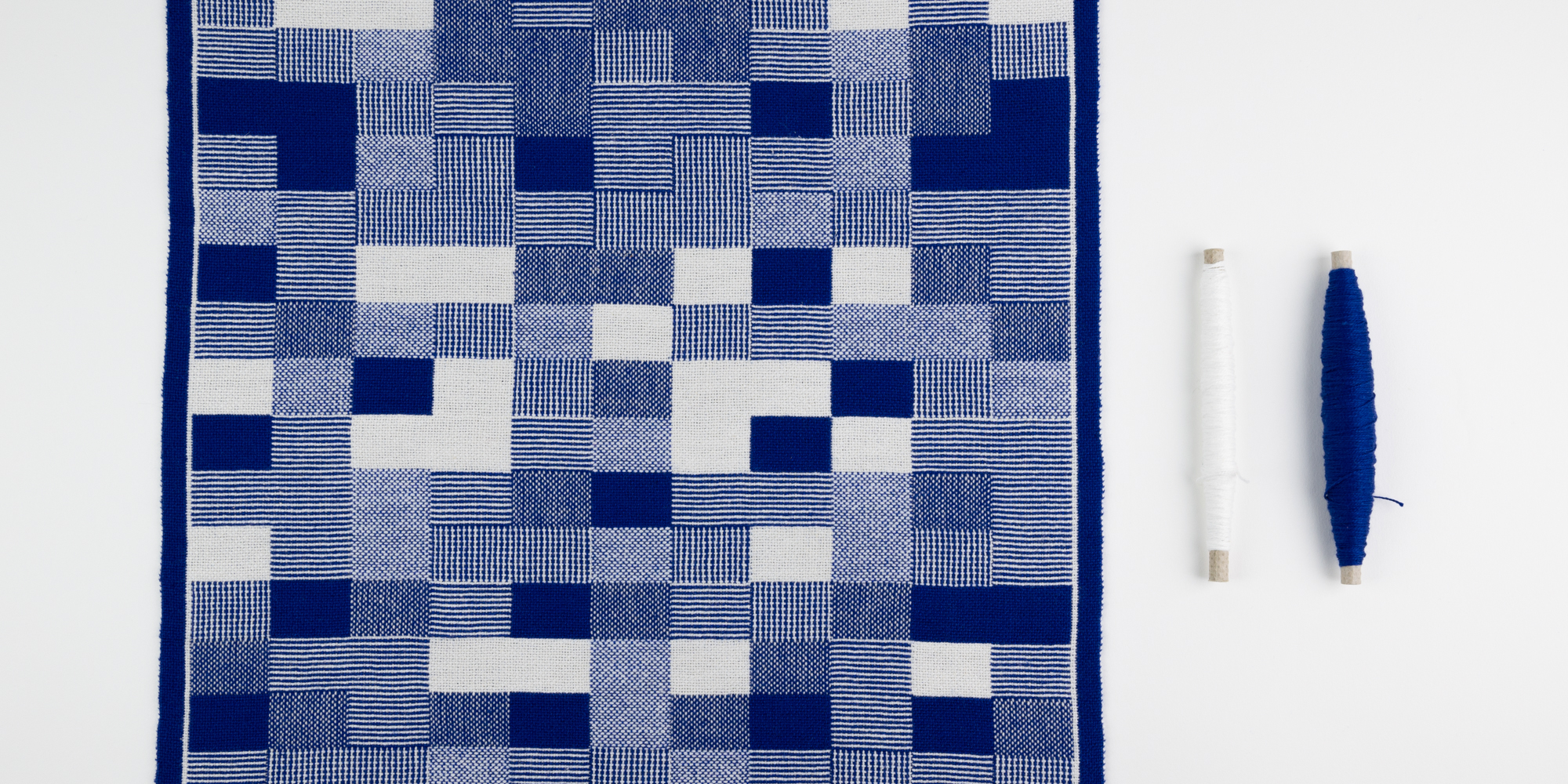
Blue White
Sample Information
Date of Creation
February 26th, 2023
Dimensions
370 mm x 380 mm x 2 mm
Weight
68 g
Culture & Context
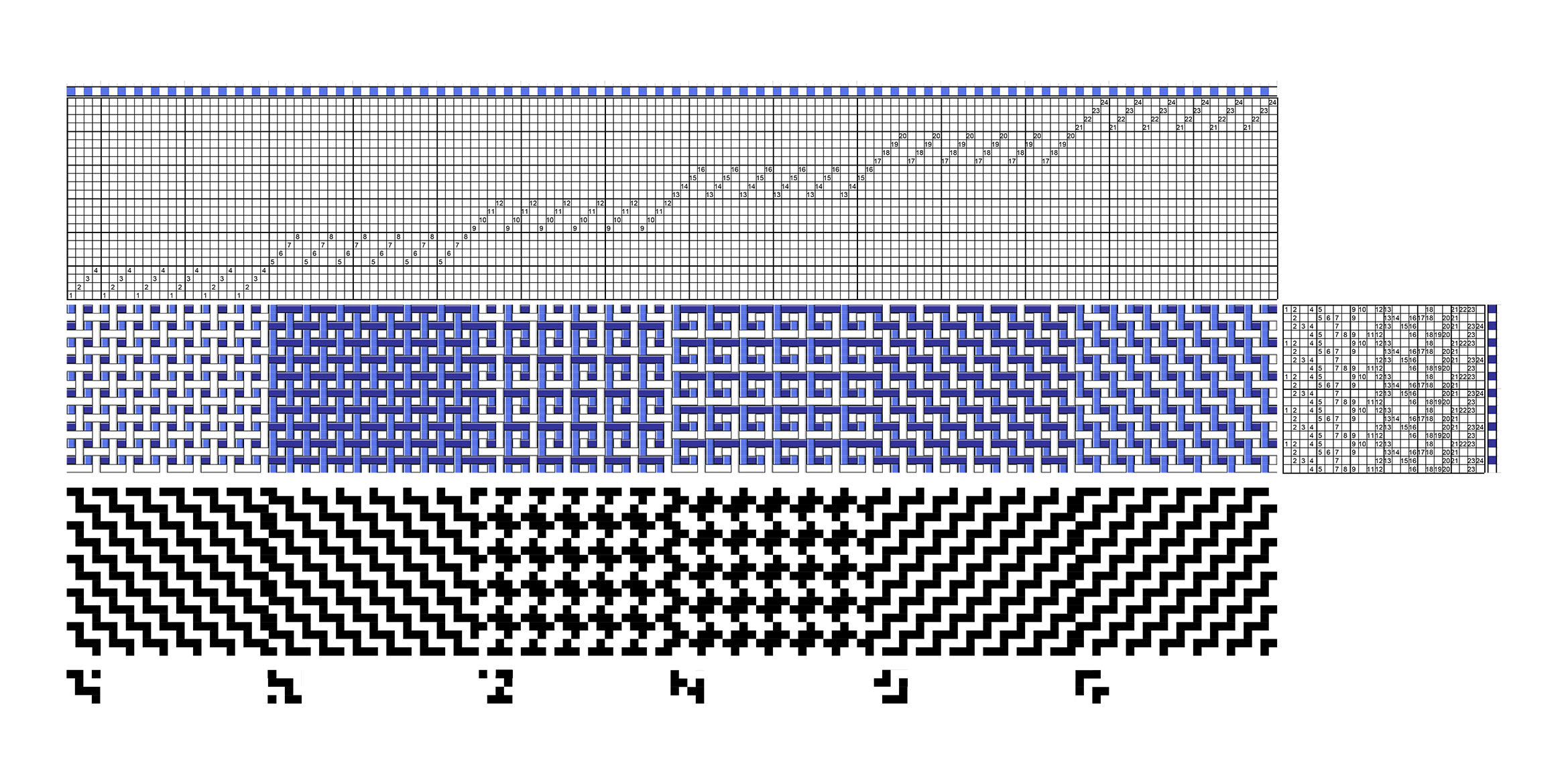
| Double-weave, in its most general sense, is a process of weaving two layers of cloth simultaneously. The interchange of these layers allows the weaver to create complex structures and patterns. Double-woven fabric dating back to the first millennium BCE has been found in Peru and in China. From these centres, knowledge of the structure spread around the world and has given rise to many different traditions of its use. In the UK it is perhaps best known in the form of Welsh ‘tapestry’ blankets, the double-layer structure being an excellent insulator.The block double weave sample shown here presents six basic plain weave interlacements which can be made from two solid colour layers. |
Process & Production
| For a handweaver the double-weaving process can be achieved through loom-control (that is, by assigning warp ends to shafts and manipulating the shafts) or by hand, or using a combination of the two approaches. This sample is woven on a 32-shaft computer dobby loom, with each individual block requiring four shafts. The design has six pattern blocks and two further blocks are used for the border. |
Recipe Details
The warp is made from two colours, royal blue and white, of 16/2 unmercerised cotton. A fairly open sett of 40 epi is used, allowing for a thicker 8/2 cotton weft in the same two colours. The web is beaten to square.
The threading is organised in blocks, which each block threaded on a straight draw on four shafts, alternating blue and white warp ends.
To create the design, each pattern block was assigned a structure at random from the six shown in the accompanying draft. The individual structure drafts were then substituted into the liftplan. This can be done using a computer program or by hand.
After weaving the fabric is washed, lightly fulled, and pressed to finish.
Credits
Craft Maker
Cally Booker
Library Contributor
Cally Booker
Photographer
Stuart Booker